【比赛】2026启航杯
misc
兄弟你好香
179 pts
听说你很会闻味道?那就来闻闻这张图片和这段音频里藏着什么秘密吧~
提交方式:QHCTF{xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
- 图片后提出来是zip
- 解压
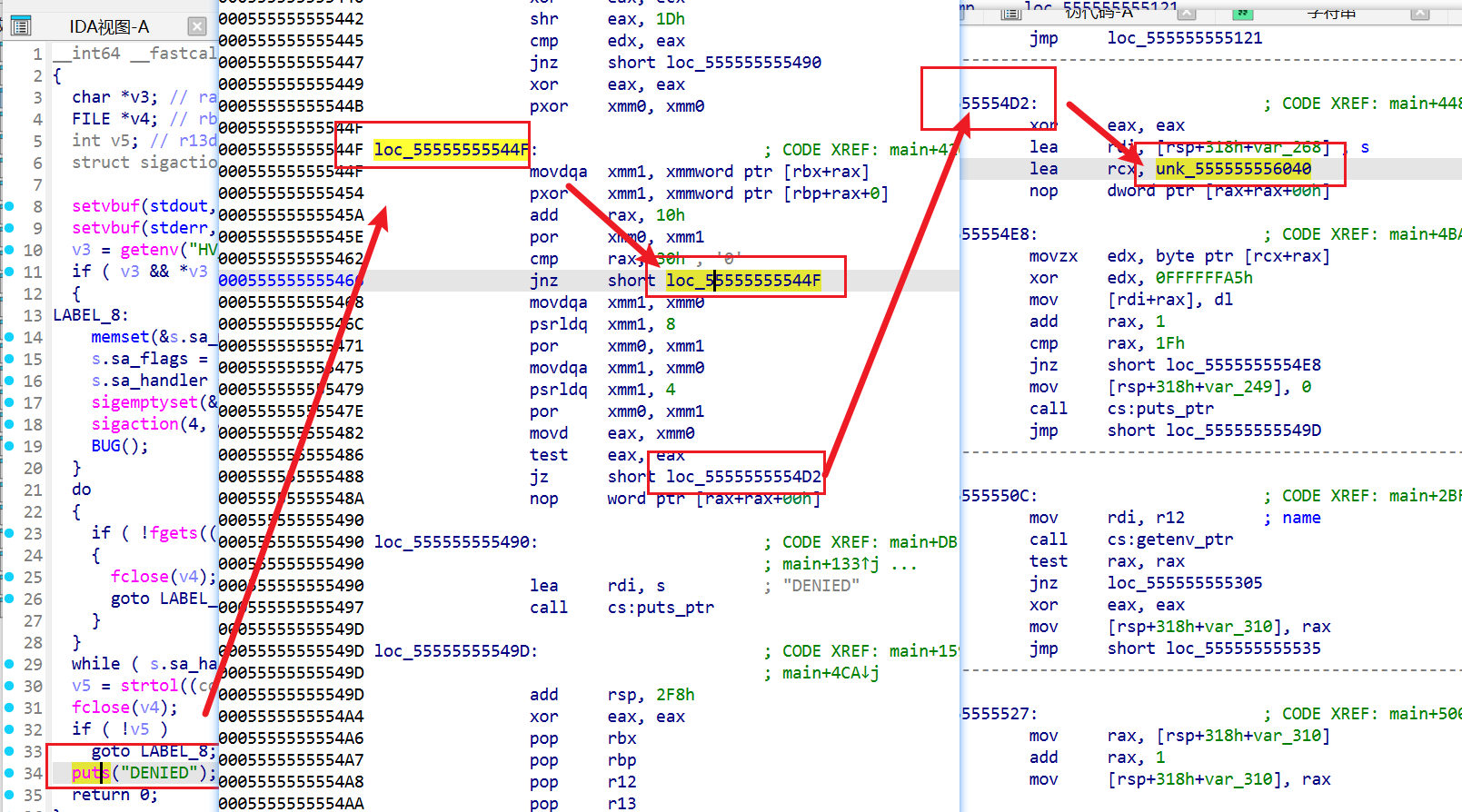
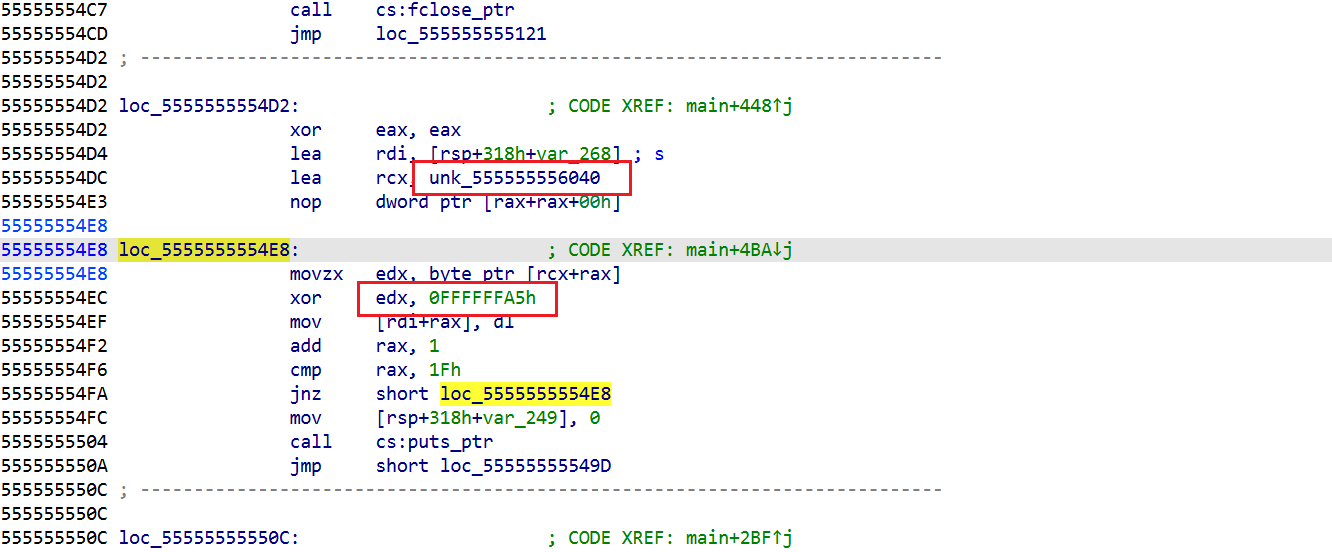
=== 兄弟,你好香啊 === |
明文密钥BrotherYouSmell!
from Crypto.Cipher import AES |
re
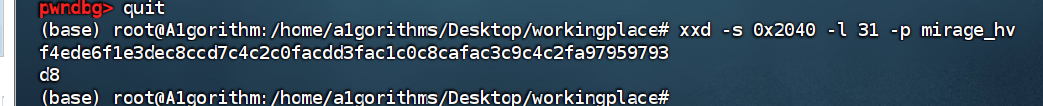
mirage_hv
提交方式:QHCTF{xxxxxxx}
enc = bytes.fromhex("f4ede6f1e3dec8ccd7c4c2c0facdd3fac1c0c8cafac3c9c4c2fa97959793d8") |
crypto
RSA Inferno
某安全公司的RSA加密系统存在多处实现缺陷。你能获得其加密的明文吗?
提交方式:QHCTF{xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
连接方式:nc [IP] [PORT]
import socket |
ai
AI_Check
某AI公司的训练数据集遭到恶意污染攻击!攻击者在数据中植入了多种隐蔽的恶意内容。作为安全工程师,你需要分析被污染的数据集,找出所有被污染的数据行,并提交修复后的CSV文件。
提交方式:QHCTF{xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- |
web
ez_ems
- 访问
/app.py下载后端源码 - 两个漏洞:
SQL 注入 (SQL Injection)
位置:search函数 (以及login函数)
代码:
search_query = request.form['search_query'] |
过滤器 basic_filter:
移除了所有空格 (replace(' ', ''))。
过滤了 UNION, SELECT 等关键字(大小写敏感,仅大写被过滤)。
过滤了 exec (大小写不敏感)。
绕过方法:
使用 小写关键字 (union, select) 绕过大写正则匹配。
使用 Tab 符 (%09) 代替空格,因为 replace(' ', '') 不处理 Tab。
Pickle 反序列化漏洞 (RCE)
位置:validate_token 函数
代码:
def validate_token(token_str): |
利用条件:Session Cookie 是经过签名的,格式为 Data.Timestamp.Signature。我们需要 secret_key 才能伪造合法的 Session。
获取 Secret Key (SQL注入)
secret_key来对 Session 进行签名,app.py中显示 key 存储在数据库 config表中。
利用/search接口进行 SQL 注入。
Payload
1'%09union%09select%091,key_value,3,4,5,6%09from%09config# |
获取到 secret_key = supersecretkey123!
- 构造 RCE Payload
由于目标环境可能阉割了 Shell 命令 (sh,bash) 或者os.system无回显,常规的反弹 Shell 或cp命令失败。
Python 纯代码执行的方式,直接利用 Pickle 读取文件内容并回显。
构造一个 Pickle 对象,在反序列化时执行类似 open('/app/flag.txt').read() 的操作,并将结果赋值给 UserToken 对象的属性(如 username)
构造逻辑
- 调用
builtins.open('/app/flag.txt')获取文件句柄。 - 调用文件句柄的
read()方法获取内容。 - 将内容作为参数构造
UserToken对象。
- 伪造 Session 并获取 Flag
- 使用获取到的
secret_key和构造好的 Pickle Payload 生成恶意的 Session Cookie替换浏览器 - 访问
/admin
pip install requests itsdangerous |
- 生成恶意 Cookie 脚本
保存以下代码为solve.py:
import pickle |
应急
3
攻击者使用反向 Shell 连接到了哪个 C2 服务器?给出 IP 和端口。
提交格式:{IP:端口}
- 搜索 WebShell 目录和命令历史
find . -type f \( -name "*.jsp" -o -name ".bash_history" -o -name "catalina*.log" -o -name "access*.log" \) | head -n 200 |
- 重点看 root/.bash_history:
cat ./root/.bash_history |
- 反弹 shell 关键词
grep -RInaE "dev/tcp|bash -i|sh -i|nc -e|ncat|mkfifo|python -c|socat|perl -e|php -r" . |
193.239.86.139:8888
- 交叉验证
在日志里搜该 IP 或端口:
grep -RIna "193.239.86.139\|8888" . |
{193.239.86.139:8888}
4
攻击者在服务器上植入了挖矿程序,要求找出挖矿程序完整路径(多个用逗号分隔)。
提交格式:QHCTF{路径1,路径2}
围绕攻击常见落地目录(/opt、/tmp、点目录)检索可执行文件,发现两处明显异常:
- /opt/.kthread/kthread
- /opt/.X11-Xtrace/kworker
这两个文件名伪装成系统线程名(kthread/kworker),且目录为隐藏目录,符合挖矿木马常见伪装手法。
file/strings: - 可执行 ELF 文件;
- 字符串中出现矿工特征(如auto.c3pool.org
- 运行后存在对外矿池连接行为
QHCTF{/opt/.X11-Xtrace/kworker,/opt/.kthread/kthread}